We will take a quick look into the different types of linking of libraries to the ELF in x86 (linux).
Linking:#
Linking - It is the process where something is being connected to something else. Suppose you call functions that is not defined in your binary and has to be used from some dependencies. There Linking comes into picture.
sample program#
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Hello World\n");
printf("Welcome to my blog\n");
}
This will just print 2 strings to the terminal. Nothing intresting and complicated. Now let us compile this with static flag set.
gcc --static test.c -o test
Code Analysis#
Now this is statically compiled. Let us try to analyse the code and see how the printf function is called.
- note: Printf is a libc function, which means it is not included in the binary and is been imported from a external dependency.
so open gdb and disassembly main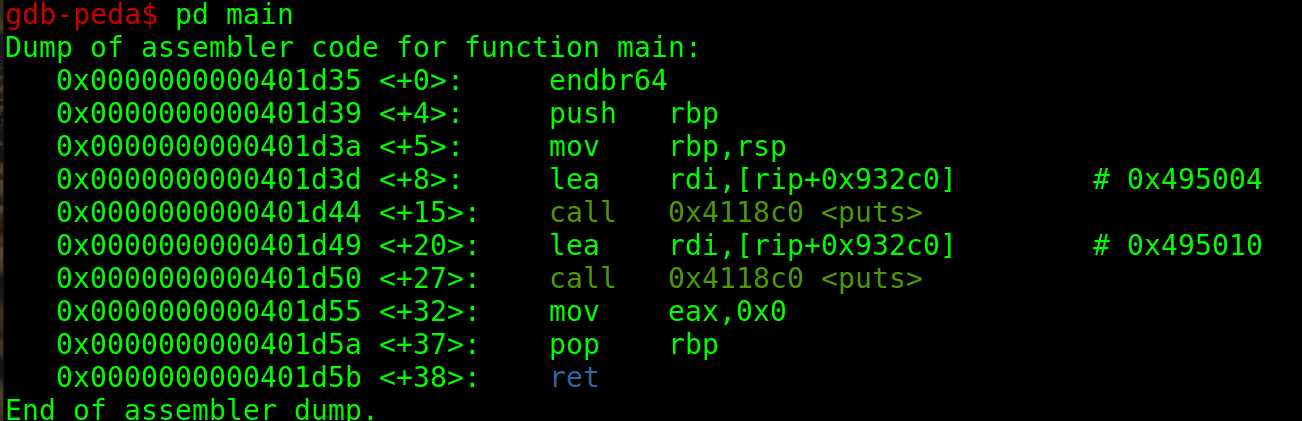
We can see that there is a normal puts. Do you remember we used printf in our function. This means the compiler plays god and decides the best function to be used in that place. Since puts is more efficient than printf it was implemented there. Instead when you use format strings in printf then puts cant be implemented in that case.
set a break point at puts and run the program.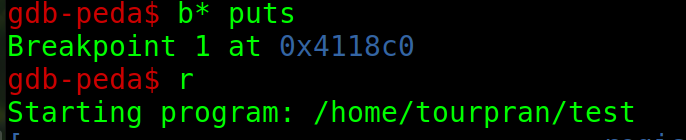
So now we see we go into the function puts. which has an address 0x4118c0. Now is this address kinda giving you an idea ? Yup ! This is our binary. If we do a vmmap (virtual memory mapping) then we can see that the address from 0x00400000 to 0x004e7000 are inside the binary. Now we can say that the puts function is inside the binary so its address is also known at runtime.
Pros and Cons#
| Advantage | disadvantage |
|---|---|
| Anybody having the binary can excecute it. There will be no dependency errors | In real Life the applications are pretty huge and need multiple dependency files. Combining all of them into one file will make the size of the binary pretty huge. |
Dynamic Linking#
Time to move on to the complicated stuff. To compile it as dynamic, you have to do a normal gcc compilation as GCC compiles everything into Dynamic linking by default.
gcc test.c -o test
Code Analysis#
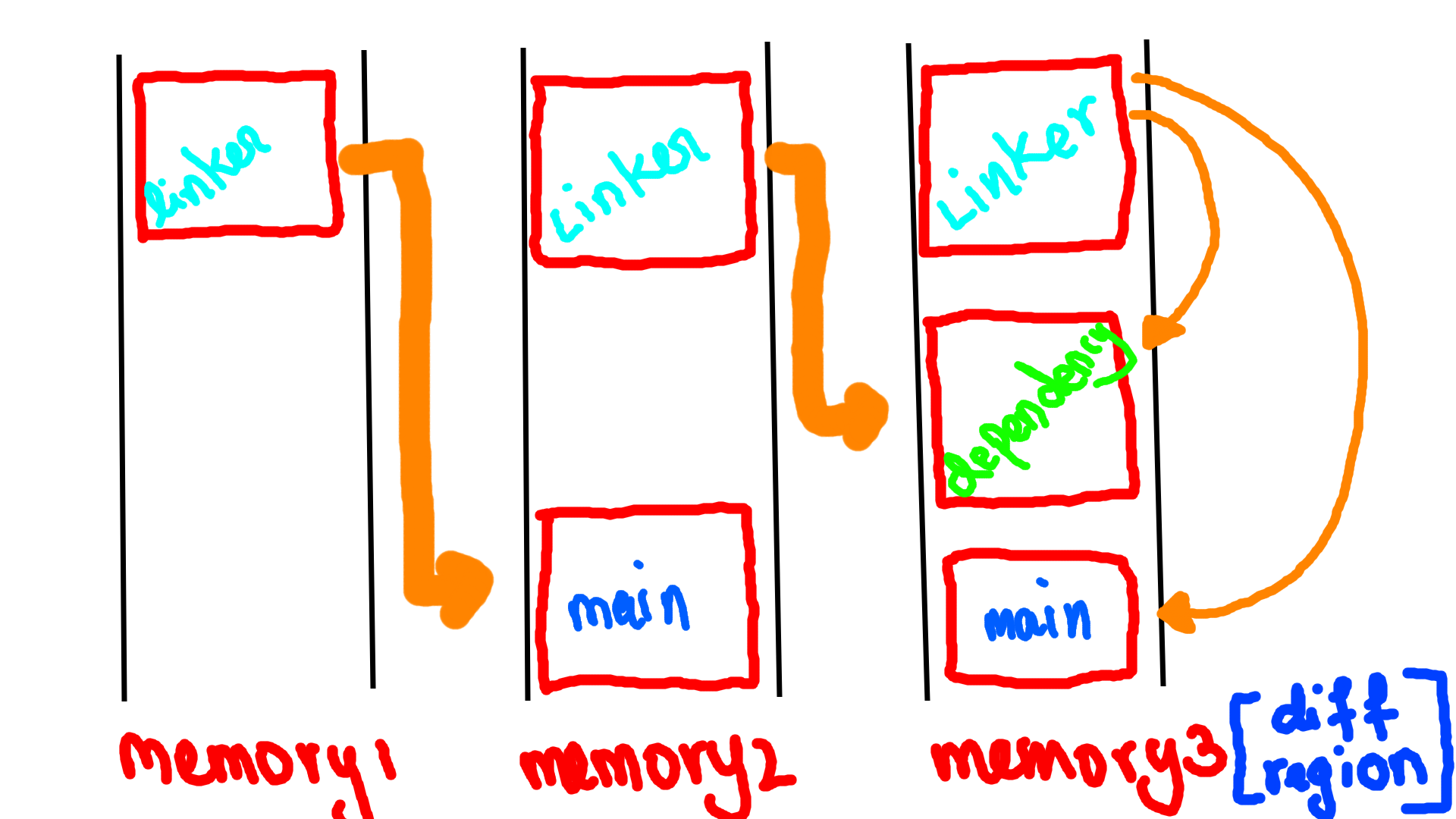
We know for a fact that the functions are not going to be inside our binary. The binary being smart will store the names of dependencies that our needed to excecute this file.
Mr. Dynamic Linker
The Dynamic Linker will link all the dependencies to the binary.
First before excecuting the elf the system will excecute interpreter, which is a program that sets up the environment for excecuting the binary, this is done with the help of .dynamic section. This program (interpreter) lies in the pt_interp segment which is created by the ld (compile-time linker).
readelf -d test
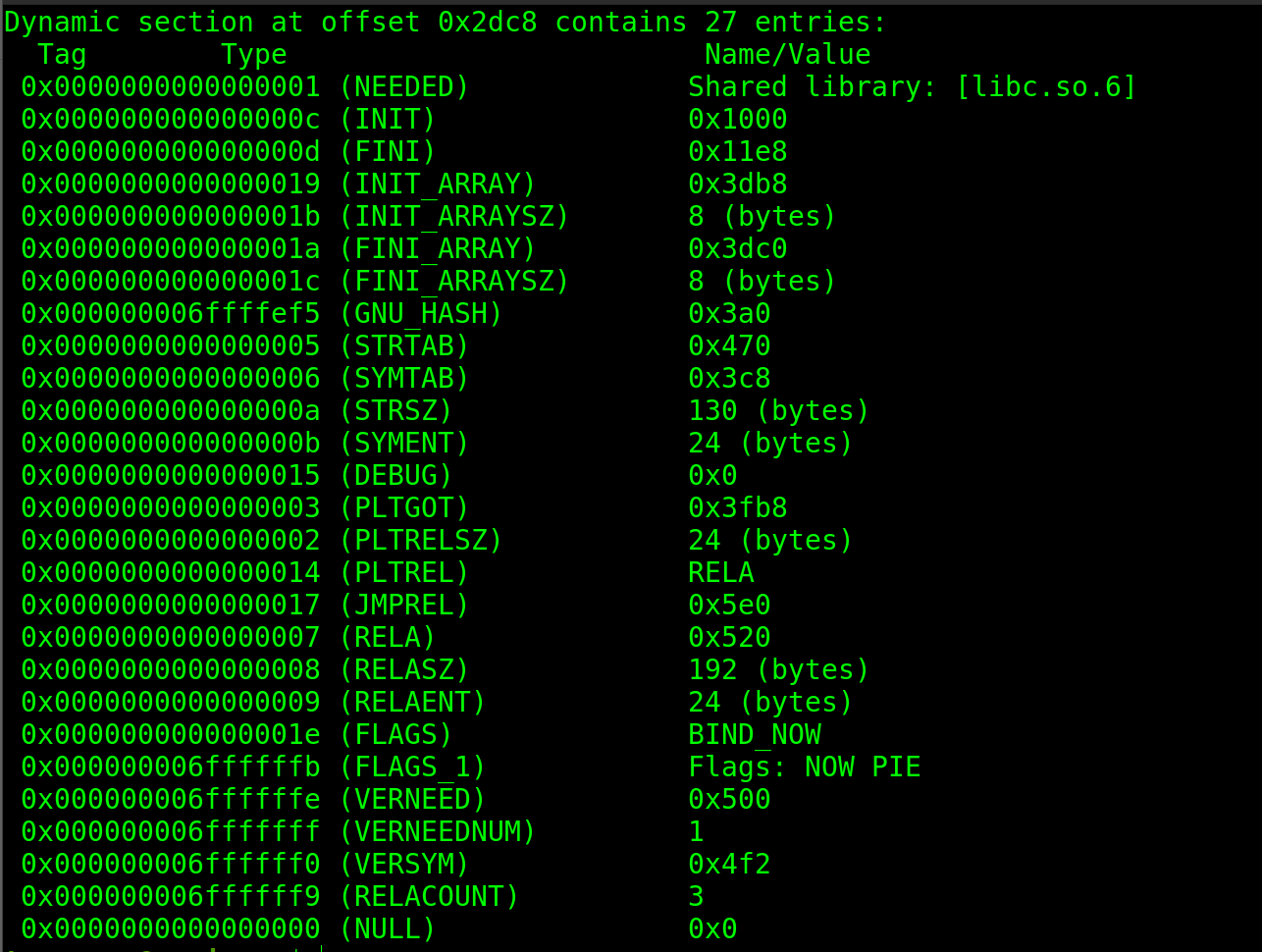
- NEEDED : contains the names of all the dependencies.
- DT_SYMTAB : Address of the dynamic symbol table. so on…
steps#
- First the dynamic linker will load the excecutable into memory.
- Next will load the dependencies which are mentioned in the binary.
- Relocation - shared libraries are loaded into non-deterministic addresses.
- then do some initialisation and go back to binary’s entry point / starting point
Pros and Cons#
| Advantage | disadvantage |
|---|---|
| People only need to have the dependencies installed once, that can be used for other binaries as well. | People who dont have the correct dependency will face a lot of problems(finding them). |
Lazy Linking#
Oops ! did I say that the linker performs all relocations. Well, thats not the case for most situations. This is where lazy linking comes into picture. So if a function is called then the dynamic linker will resolve the address for the function. Hence the name “Lazy” Linking. This awesome work is done by the GOT and PLT. (Next blog)
Reference:#
Really cool blog which made me understand this concept. intezer
