So the ELF or Excecutable and Linkable format are programs or binaries that are used in linux systems. ELFs contain 3 components namely:
- ELF Headers
- ELF Segments
- ELF Sections
Need:
A good reason to learn ELF format is it helps you to understand things easily when you do binary analysis or when you are curious to know how the Operating System works. There are several reasons why you need to know them …
ELF Headers
Firstly we will be looking at ELF which are 64 bits, dynamically linked, not stripped.

Lets look at the ELF header with readelf.
readelf -h binary
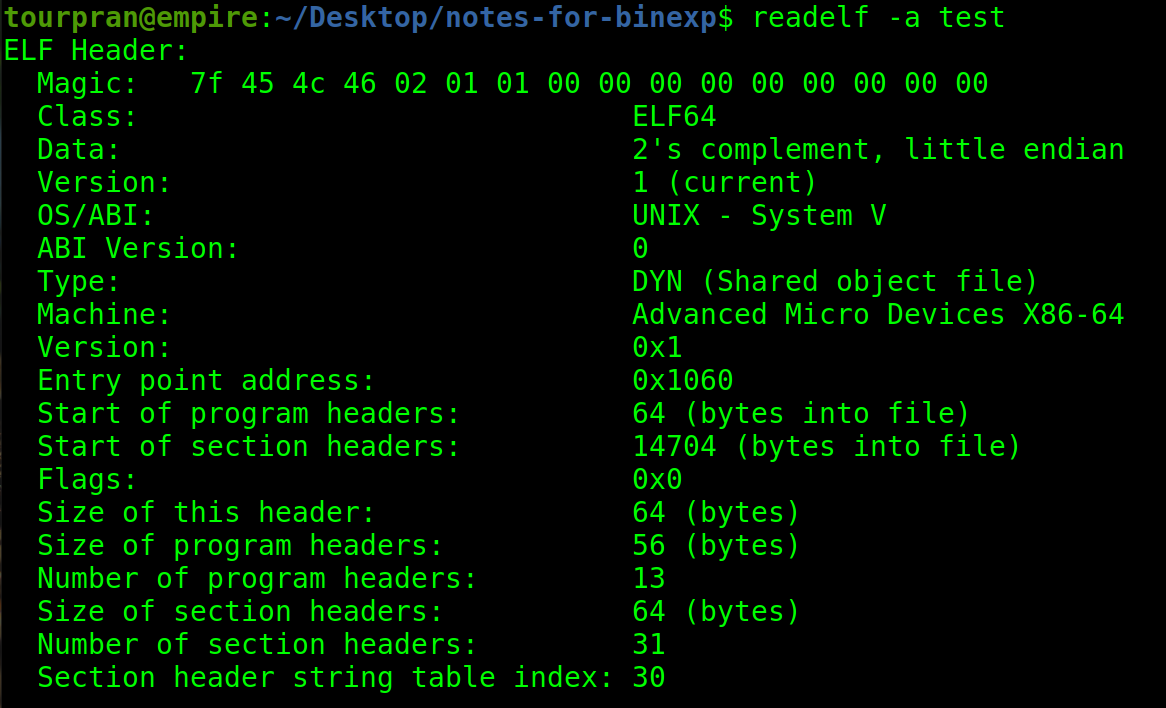
magic
We can see from the image that our header / binary starts with the magic bytes Magic: 45 4c 46 which corresponds to ELF in ascii. This magic bytes tell the file command that this is an Excecutable and Linkable Format.
Class
This binary has a class of 64 bits because when I compiled, it was in a 64 bit machine so by default it will be 64 bits. Inorder to compile a 32 bit binary we need to give the -m32 flag to gcc.
Data
| Little Endian | Big Endian |
|---|---|
| The bytes of a word are arranged from right to left | The bytes of a word are arranged from left to right |
| The address of the word (assume 4 bytes) will point to 4 th bytes | The address of that word (assume 4 bytes) will point to the 1st bytes |
So in our case its little endian and most 64 bit amd processors compile it in little Endian.
OS/ABI
Nothing to tell about OS (Operating System). I compiled this is my laptop which is Linux hence Unix.
Machine
Tells us we have x86 architecture with 64 bits.
type
Not sure why its DYN(Shared Object). It should have been EXEC (Executable file).[will update soon].
Rest
Rest of the information is regarding addresses and Size of sections and headers.
Segments (aka Program Headers)
readelf -h ``binary``
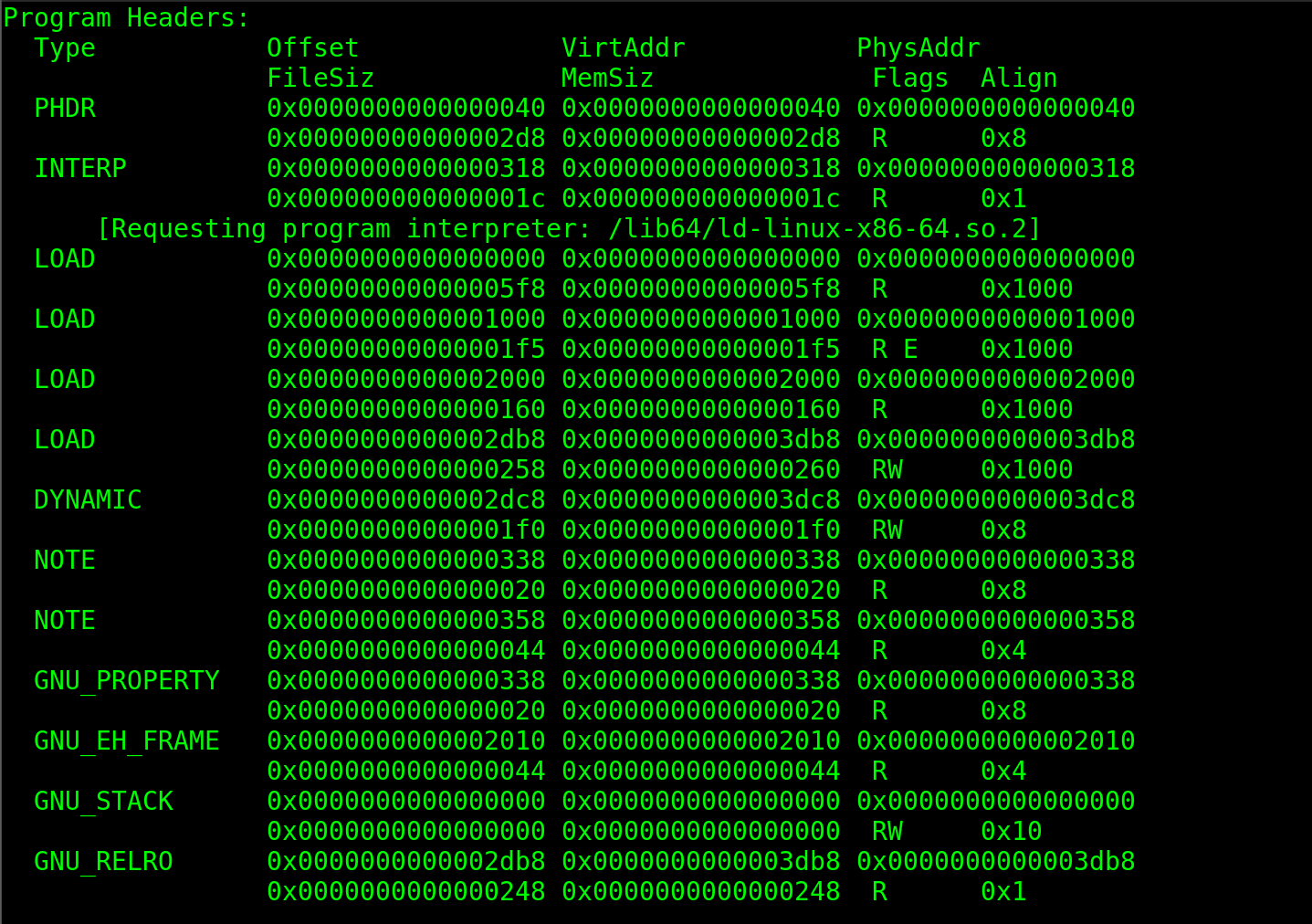
This is a array of structures. Each describes the segments. The segments are used to tell, how to create a memory image when the binary is excecuted. When the Kernel sees these segments it will map them into the Virtual Memory with the help of mmap system call.
PHDR
Tells the location of the Program header itself if its present.
interp
specifies the location and size of a null-terminated path name to invoke as an interpreter
interpreter
* It is a program that excecutes certain specified instructions [not to worry now].
dynamic
This segment specifies the information needed for the dynamic linking process.
GNU_EH_FRAME
This stores exceptional handlers. When things go wrong this area can deal with it.
GNU_STACK
- stack
- * This is just a place where things can be stored during runtime.
This GNU_STACK is responsible for the stack being excecutable. If this is not there then by default stack will be excecutable. If stack is enabled then user input can also be excecuted and can lead to a great havoc.
ELF Sections
This is also commonly called as section headers. This has the information needed for linking a target object file (dependencies) to the binary. This is needed on linktime but not on runtime.
Common Sections
- .text: This section contains the code for the binary.
- .data: Holds all the initialised data.
- .rodata: Holds the initialised read-only data.
- .bss: Contain all the uninitialized data.
- .plt: PLT (Procedure Linkage Table) is useful when it comes to getting address of functions in dynamically linked libraries.
- .got: Contains all the resolved address of the functions from the dependecies.
- .dynamic: Holds all needed information for dynamic linking.
- .dynsym: table dedicated to dynamically linked symbols.
- .strtab: string table of .symtab section.
- .dynstr: string table of .dynsym section.
- .interp: RTLD embedded string.
END
Hope you understood some basic concepts related to the ELF file format.
